
Technology
SUDOSCAN® Device
The SUDOSCAN® system comprises of a touchscreen computer, a docking station for the hand and foot, and SMART electrodes™.
SUDOSCAN provides a quick and non-invasive stimulation of sweat glands to assess small nerve fibers (C fibers) within 3 minutes.
What does SUDOSCAN measure?
SUDOSCAN® offers a stimulation of the sweat glands in the hands & feet that assess small nerve fibers.
SUDOSCAN® is a cutting-edge test designed to evaluate sweat function with unparalleled accuracy. By targeting the small nerve fibers in the peripheral nervous system that control the sweat glands, SUDOSCAN® delivers quick and reliable results. With just four electrodes and a computer, patients can complete the test in under three minutes, and the device can assess the function of C fibers, which play a crucial role in sweat production.
Learn more about how SUDOSCAN® can help diagnose, measure and monitor sweat-related conditions today.
SWEAT GLAND FUNCTION
A RELIABLE INDICATOR FOR PERIPHERAL AUTONOMIC NEUROPATHY
The sweat glands in our bodies are regulated by small sympathetic C-fibers, and abnormalities in sweat function can be an early sign of distal small fiber neuropathies. Quantitative assessment of sweat response has been suggested as a reliable indicator of autonomic failure and early regeneration of small fibers. In fact, diabetes is one of the most common identifiable causes of small fiber neuropathy. Learn more about the importance of sweat function testing and its potential implications for neuropathy diagnosis and management today.

The American Diabetes Association (ADA) recognizes that sudomotor (sweat) dysfunction is a significant clinical manifestation of diabetic autonomic neuropathy. In addition, evaluating autonomic dysfunction can help identify patients at high risk for cardiac autonomic neuropathy, which carries a significant risk of morbidity and mortality. By measuring motor, sensory, and autonomic function, healthcare providers can gain a more comprehensive understanding of neuropathy and improve patient outcomes. Learn more about the importance of autonomic function testing for diabetic neuropathy today.
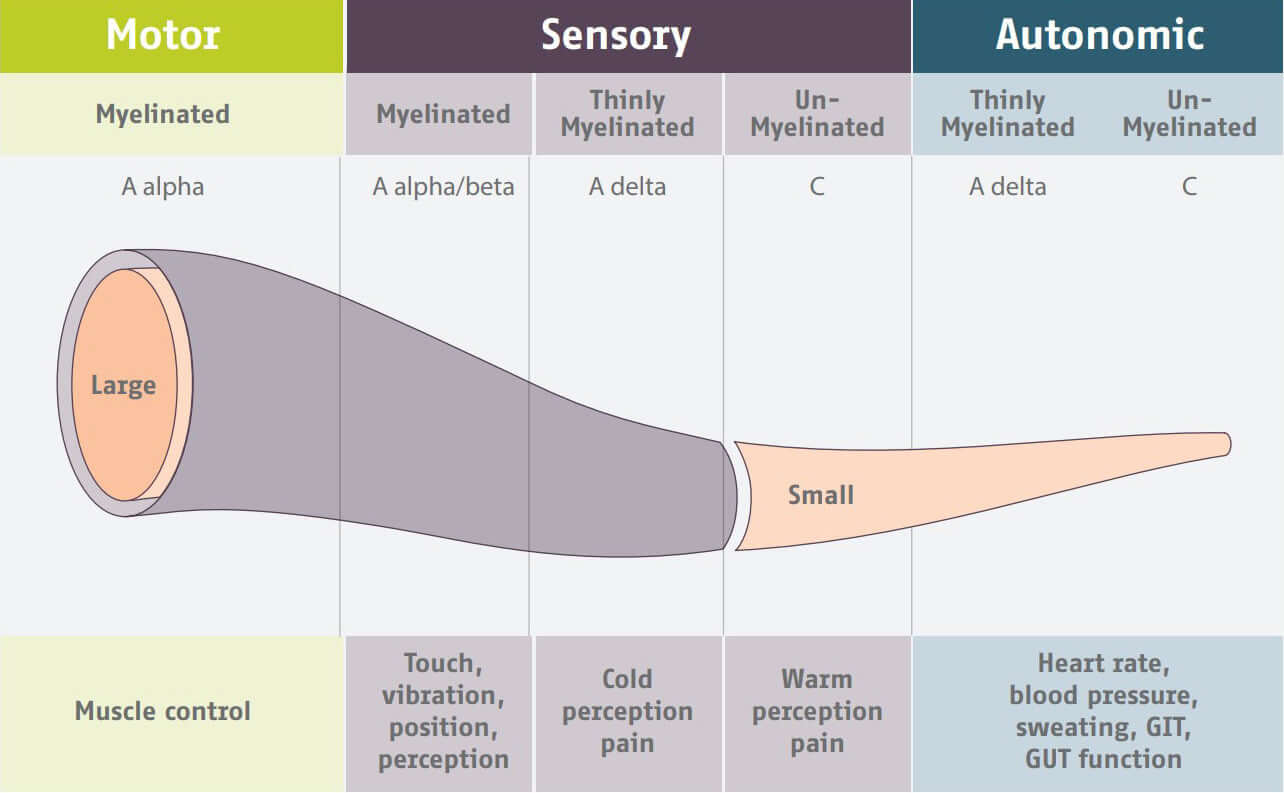
The peripheral nervous system is made of large and small fibers. The small, un-myelinated C-fibers are in charge of autonomic functions such as sweating.

Small fiber autonomic nerves regenerate more quickly than the large fiber nerves upon capsaicin application

What are the alternatives?
The use of skin biopsy to measure Intraepidermal Nerve Fiber Density (IENFD) or Sweat Gland Nerve Fiber Density (SGNFD) is an accepted surrogate measure of small fiber neuropathy. While skin biopsy is well accepted by the medical community, it has certain limitations as: invasiveness, risk of infection, bleeding, and a limited number of laboratories that can process the sample [6]. The Quantitative Sudomotor Axon Reflex Test (QSART) measures sweat response under controlled humidity and temperature conditions. It requires fairly expensive equipment and is available in few centers.
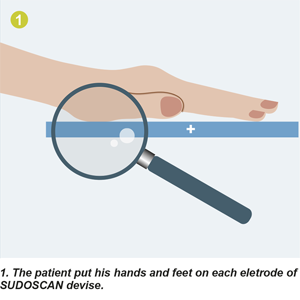
The process
- The patient is asked to put his hands and feet on large electrodes
- A small electric tension is applied to the surface to stimulate the sweat glands
- The results of the response to this stimulation are expressed as :
- Electrochemical Skin Conductance for SUDOSCAN®, indicating the presence and severity of the small fiber peripheral autonomic neuropathies;
- Percentage of risk for EZSCAN indicating a risk to develop diabetes.


How does it work?
Small fiber neuropathy can lead to degeneration of nerve fibers and a reduction in sweat gland innervation, ultimately affecting sudomotor function. With SUDOSCAN®, you can measure the concentration of chloride ions produced by sweat gland activity in a non-invasive and efficient manner. Using stainless steel sensor electrodes, a low-voltage current (<4V) is applied to the hands and feet, extracting chloride ions from the densely concentrated sweat glands on the palms and soles. Since the stratum corneum serves as an insulator, the ions can only pass through the sweat ducts, ensuring accurate measurement of sweat gland function. Any electrochemical reaction between the chloride ions and the sensor plates is detected and measured, allowing for comprehensive assessment of sudomotor function. Discover the benefits of SUDOSCAN® for managing neuropathy today.
What is measured.
SUDOSCAN® is an advanced tool for recording Electrochemical Skin Conductances (ESC) in the hands and feet, which are generated by the current associated with the applied voltage. Reduced ESC levels may indicate a loss of sweat glands or their innervations, highlighting potential issues with sudomotor function. By measuring ESC in a non-invasive and efficient manner, SUDOSCAN® can help healthcare providers better assess neuropathy and develop more targeted treatment plans. Learn more about the importance of measuring ESC and how SUDOSCAN® can improve your neuropathy management today.
Experience quick and accurate evaluation of sudomotor function with SUDOSCAN®. This innovative testing tool measures the ability of sweat glands to release chloride ions in response to electrochemical activation on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet - areas with the highest concentration of sweat glands. With results available in under three minutes, SUDOSCAN® provides a fast and efficient way to assess sudomotor function with unparalleled accuracy. Discover how SUDOSCAN® can help improve diagnosis and monitoring of sweat-related conditions today.
Clear results
- Simple
- Quantitative
- Accurate
Thanks to its ergonomic touch screen and detailed graphics, this device offers a user-friendly way to visualize and interpret test results. With an immediate quality check, you can trust the reliability of the data. Results are presented with a simple color code: green means no neuropathy, yellow indicates a moderate level, and orange signals a more severe neuropathy. Get clear and accurate results in no time with this advanced testing tool.
Get a detailed understanding of your neuropathy with this advanced testing tool. The device displays actual numerical values of the Electrochemical Skin Conductance (ESC) for each hand and foot, providing insight into the severity of the condition. This measure can also be used to track changes over time and evaluate the effectiveness of treatment or other interventions. With accurate and reliable results, this device is an essential tool for managing neuropathy.
Identify the type of peripheral neuropathy with ease using this advanced testing tool. By measuring the symmetry between the right and left sides of the body, this device offers valuable insights into the nature of the condition. Additionally, the device allows for easy follow-up of neuropathy progression, enabling you to track changes and adjust treatment plans accordingly. With accurate and reliable results, this device is an essential tool for managing neuropathy and improving patient outcomes.
Simple results obtained in 3 minutes
The results are displayed automatically.
If the score is high, this indicates no sign of sudomotor dysfunction and no autonomic neuropathy.
If the score is low, this indicates a sudomotor dysfunction and a neuropathy.


SUDOSCAN® IN NEUROLOGY
The Effectiveness of SUDOSCAN® in Neurology
Peripheral neuropathy is a condition that arises from damage to the peripheral nerves, including small fiber neuropathy affecting small myelinated nerves (Aδ) as well as unmyelinated nerves (unmyelinated C fibers). The damage to small somatic and autonomic fibers can lead to thermal and pain perception problems, and dysfunction of the cardiovascular, respiratory or digestive systems.
Peripheral neuropathy can be associated with various conditions such as diabetes, metabolic or neurological disorders, and infections. Certain medications or excessive alcohol consumption may also contribute to its development.
It is possible for peripheral neuropathy to occur in the early stages of disease, highlighting the importance of early detection to enable effective management and reduce the risk of advanced complications.
SUDOSCAN® has been utilized to assess small fiber neuropathies in various diseases and therapeutic areas that involve neurological complications, including:
- Hereditary amyloidosis, AA, wild type
- Covid-19
- Hepatitis C
- Epilepsy
- Fabry disease
- Parkinson’s disease
- Autoimmune small fiber neuropathy
- Fibromyalgia
- Lewy body dimentia
- Narcolepsy
- Sjörgen’s syndrome
- Pure autonomic failure

SUDOSCAN® AND DIABETES
Detecting Diabetic Neuropathy at an Early Stage
Multiple studies have demonstrated the efficacy of SUDOSCAN® in early detection of diabetic neuropathy. With its ability to accurately assess sudomotor function, Sudoscan can aid in the management of diabetes complications such as diabetic foot and cardiac autonomic neuropathy, as well as help healthcare providers monitor disease progression over time. By utilizing SUDOSCAN® as a diagnostic tool, providers can develop more targeted treatment plans and improve patient outcomes. Learn more about the benefits of SUDOSCAN® in the early detection and management of diabetic neuropathy today.

The Importance of Managing Diabetic Complications
Type 2 diabetes can progress silently, without noticeable symptoms, and as a result, many cases remain undiagnosed until complications appear. In fact, up to one third of all cases may go undetected. Even more concerning, epidemiologic evidence suggests that irreversible tissue damage from complications like peripheral vascular disease, nephropathy, retinopathy, and neuropathy may have already set in by the time of diagnosis for a substantial number of patients.
Neuropathy is particularly common in patients with diabetes, with 60-70% experiencing some form of it.
Diabetic Autonomic Neuropathy (DAN) is a serious and common complication that can affect the entire autonomic nervous system. It often precedes other complications and can manifest as dysfunctions in multiple organ systems, including cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, genitourinary, ocular, and sudomotor. Early detection and management of DAN is critical to improving patient outcomes and preventing further complications. Learn more about how Sudoscan can help detect diabetic neuropathy and other autonomic dysfunctions today

SUDOSCAN® IN ONCOLOGY
The efficacy of SUDOSCAN® has been demonstrated in the field of oncology.
Peripheral neuropathy arises from damage to the peripheral nerves, which can affect small and myelinated nerves (Aδ) as well as unmyelinated nerves (C fibers). This damage can cause small somatic and autonomic fibers to malfunction, which can lead to issues with thermal and pain perception, as well as cardiac, pulmonary, or enteric functions. Several diseases, including diabetes, neurological or metabolic disorders, and infections, can result in peripheral neuropathy. Additionally, certain medications, such as chemotherapy, and alcohol consumption can also cause this complication.
Early detection of peripheral neuropathy can be crucial in managing patients and preventing advanced complications. SUDOSCAN has shown clinical effectiveness in the field of oncology, specifically in detecting chemotherapy-induced polyneuropathy (CIPN). This can aid physicians in managing treatment and limiting the worsening of neuropathy, ultimately improving the quality of life for patients undergoing chemotherapy or in palliative care.
SUDOSCAN® can facilitate the detection of oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy, a painful complication that can arise from treatment, and aid in treatment management.
A study conducted by Delmotte et al from Saint Joseph Hospital, Paris, used SUDOSCAN to assess Oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy (OIPN). The study aimed to determine the potential of Electrochemical Skin Conductance (ESC, measured with SUDOSCAN) in diagnosing OIPN. The study included 36 patients with cancer who were treated with oxaliplatin for at least three months and suffered from clinical OIPN. Low ESC measurements indicate decreased sudomotor nerve function, while a Neuropathic Pain Symptom Inventory (NPSI) score > 0 indicates painful symptoms. The main finding of the study was the correlation between the NPSI score and ESC scores in the hands (rho value = -0.69, p < 0.0001) and feet (rho value = -0.79, p < 0.0001). Neuropathic patients with painful symptoms had lower ESC values than those without painful symptoms (p = 0.0003 and p < 0.0001 for hands and feet, respectively).
These preliminary results suggest that ESC measured with SUDOSCAN could be a useful objective marker of painful OIPN and could complement the use of subjective clinical scales.


FOLLOW UP WITH SUDOSCAN®
Patient outcomes have been monitored using SUDOSCAN®.
SUDOSCAN® is highly valuable in clinical practice for longitudinal follow-up and patient management. Its exceptional reproducibility and repeatability enable physicians to monitor patient outcomes over time, evaluate the advancement of neuropathy, and gauge the efficacy of lifestyle modifications or medication.
This section presents three cases that demonstrate the practical use of SUDOSCAN® in monitoring patients' progress over time in various clinical settings.
Monitoring the efficacy of vitamin B12 supplementation in diabetic neuropathy using SUDOSCAN®.
A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study investigated the effect of oral vitamin B12 supplementation on type 2 diabetes patients with diabetic neuropathy by measuring sudomotor function using SUDOSCAN®. The study included 90 patients with well-controlled type 2 diabetes and both peripheral and autonomic diabetic neuropathy, who were tested to evaluate neurophysiological parameters, sudomotor function, pain score, and quality of life. After 12 months of oral B12 supplementation with 1 mg/day of methylcobalamin, there were increased plasma B12 levels and significant improvements in all evaluated parameters, including neurophysiological parameters, sudomotor function, pain score, and quality of life. SUDOSCAN® was used to monitor the sudomotor function during the study.
Table: Changes in indices from baseline to follow-up in both groups.


SUDOSCAN® Technology
SUDOSCAN® is a non-invasive medical device that measures sweat gland function by assessing the electrical conductance of chloride ions. It uses a small direct current applied to both hand and foot sensor plates to measure the conductance of chloride ions, which serves as a quantitative biomarker for sweat gland function in relation to sweat gland innervation.
This technology provides objective and reproducible measurements of sudomotor function, which can be useful for the diagnosis and monitoring of peripheral neuropathies, including diabetic neuropathy and chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy.
SUDOSCAN® Patents
- “Electrophysiological analysis system and method” (US Patent No. US 8965497B2, European Patent No. EP 1898783B1),
- “Electrophysiological analysis system” (US Patent No. US 8655443B2, European Patent No. EP 2124736B1),
- “Assessment of sudomotor function for peripheral diabetic neuropathy evaluation” (US Patent No. US 8934954B2)
- “Improved electrophysiological analysis system” (US Patent No. US 9636036B2, European Patent No. EP 2890294B1).
CERTIFICATION SYSTEM
ISO 13485:2016

SUDOSCAN® System

SUDOSCAN® Mobility Kit

SUDOSCAN® Touch Screen

Dual SMART Electrodes™

Mobillity Cleaning Kit

SUDOSCAN® Complete setup using easy start instructions.
Setting up your SUDOSCAN® device and applications is made easy with our step-by-step instructions. You don't need to be tech-savvy; simply follow the instructions in the easy setup guide and your device will be configured and ready for your first patient.

SUDOSCAN® Smart Electrode™
The SUDOSCAN® Hand & Foot Docking Systems utilize both reusable and disposable Smart Electrodes™ sensors. These electrodes are designed for easy replacement using a simple slide and lock mechanism. They are compatible with our portable hand and foot docking units, making it convenient to perform sudomotor function tests on the go.

SUDOSCAN & Smart Electrodes™ FDA cleared patented technology.
The SUDOCAN® device is covered by the following patents and designs:
“Electrophysiological analysis system and method” (US Patent No. US 8965497B2, European Patent No. EP 1898783B1),
“Electrophysiological analysis system” (US Patent No. US 8655443B2, European Patent No. EP 2124736B1),
“Assessment of sudomotor function for peripheral diabetic neuropathy evaluation” (US Patent No. US 8934954B2),
“Device for measuring electrophysiological data with impoved reliability” (US Patent No. US 10537272B2),
"Electrodes" (US Designs No. D815746 and D796681, European Designs No. EU0028464100001S and EU0028464100002S)

The video highlights the benefits of using SUDOSCAN® as a quick and non-invasive tool for assessing sudomotor function, detecting early neuropathy, monitoring patient progress, and guiding treatment decisions. It also emphasizes the utility of SUDOSCAN® in various clinical settings, including endocrinology, oncology, cardiology, and neurology. Overall, SUDOSCAN® provides a valuable tool for improving patient care and outcomes.



